Small business taxes can be a complex maze for entrepreneurs. At SmallBizToolbox, we understand the challenges you face in navigating your tax obligations.
This guide breaks down the essential taxes you need to pay as a small business owner in Australia. We’ll cover income tax, GST, payroll tax, and superannuation to help you stay compliant and avoid costly mistakes.

How Much Income Tax Will Your Small Business Pay?
Small business owners in Australia must navigate a complex web of income tax obligations. The amount you’ll pay depends largely on your business structure and annual turnover.
Sole Trader Income Tax
As a sole trader, you report your business income on your individual tax return. For the 2023-24 financial year, you pay no tax on the first $18,200 you earn. After that, tax rates increase progressively. You’ll pay 19% on income between $18,201 and $45,000, and 32.5% on income between $45,001 and $120,000.

The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) reports that approximately 60% of small businesses operate as sole traders. This structure offers simplicity but can lead to higher tax rates as your income grows.
Company Tax Rates
If you’ve set up a company, you pay a flat rate of 25% on all taxable income, provided your aggregated annual turnover is less than $50 million. This rate applies from the 2021-22 income year onwards.
Companies with higher turnovers face a 30% tax rate. While this might seem steep, the company structure can offer tax advantages for businesses with substantial profits.
Partnership Taxation
Partnerships don’t pay income tax. Instead, each partner reports their share of the partnership income on their individual tax return. This can benefit partners with different tax situations or if the business has losses to distribute.
Tax Planning Strategies
Tax planning is essential regardless of your structure. Consider these strategies:
- Claim all eligible deductions. The ATO allows deductions for most expenses directly related to earning your income.
- Use the $30,000 instant asset write-off for eligible purchases.
- If you’re a sole trader, explore the small business income tax offset (which can reduce your tax by up to $1,000).
- For companies, investigate whether you qualify for the lower 25% tax rate.
The Impact of Business Structure on Taxation
Your choice of business structure significantly affects your tax obligations. Sole traders might face higher individual tax rates but enjoy simpler reporting. Companies benefit from a flat tax rate but must comply with more complex regulations. Partnerships offer flexibility in income distribution but require careful planning to maximize tax efficiency.
As we move forward, let’s examine another critical tax consideration for small businesses: the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
How Does GST Impact Your Small Business?
When to Register for GST
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) affects most small businesses in Australia. You must register for GST if your current GST turnover – your turnover for the current month and the previous 11 months – totals $75,000 or more ($150,000 or more for non-profit organizations). Ride-sharing drivers need to register regardless of turnover.

You can opt to register for GST even if you’re below the threshold. This might benefit you if you primarily deal with other GST-registered businesses, as it allows you to claim GST credits on your purchases.
Calculating and Reporting GST
Once registered, you’ll add 10% GST to most goods and services you sell. You’ll also claim credits for the GST included in your business purchases. The difference between these amounts is what you pay to (or receive from) the ATO.
You’ll typically report GST quarterly through your Business Activity Statement (BAS). Some businesses may qualify for annual reporting. The ATO’s online services streamline this process, but many small business owners find that accounting software (like Xero or MYOB) simplifies GST tracking and reporting.
GST Exemptions and Special Rules
Not all goods and services attract GST. Common exemptions include:
- Most basic foods
- Some education courses
- Some medical and health services
- Certain financial supplies
Specific industries have unique GST rules. The tourism industry, for example, has special GST rules for international travelers. Real estate businesses must understand GST withholding rules for new residential properties.
Tools and Resources for GST Compliance
Many small business owners find GST compliance challenging. That’s why it’s important to use tools and resources that help navigate these complexities. From GST calculators to BAS preparation guides, the right resources can simplify your tax obligations.
Industry-Specific GST Considerations
Different industries face unique GST challenges. For instance:
- Retailers must correctly apply GST to their products (which can be complex for businesses selling both GST-free and GST-inclusive items).
- Exporters often deal with GST-free sales but still need to track and report these transactions.
- Construction businesses face specific GST rules for new residential properties and substantial renovations.
Understanding these industry-specific nuances is key to proper GST management. As we move forward, let’s examine another critical tax consideration for small businesses: payroll tax and superannuation obligations.
How Payroll Tax and Superannuation Impact Your Business
Understanding Payroll Tax Across States
Payroll tax is a state-based tax on wages paid by employers. The thresholds and rates differ across Australia, which makes it important to know your local requirements. In New South Wales, the threshold for the 2023-24 financial year stands at $1,200,000, with a 5.45% rate above this amount. Victoria, however, has a $700,000 threshold and a 4.85% rate.
Small businesses often overlook payroll tax, but it can become a significant expense as you grow. To manage this:
- Keep a close eye on your wage bill, especially near the threshold.
- Include payroll tax in your pricing and financial forecasts.
- Consider the implications for interstate expansion (each state has different rules).
Navigating Superannuation Obligations
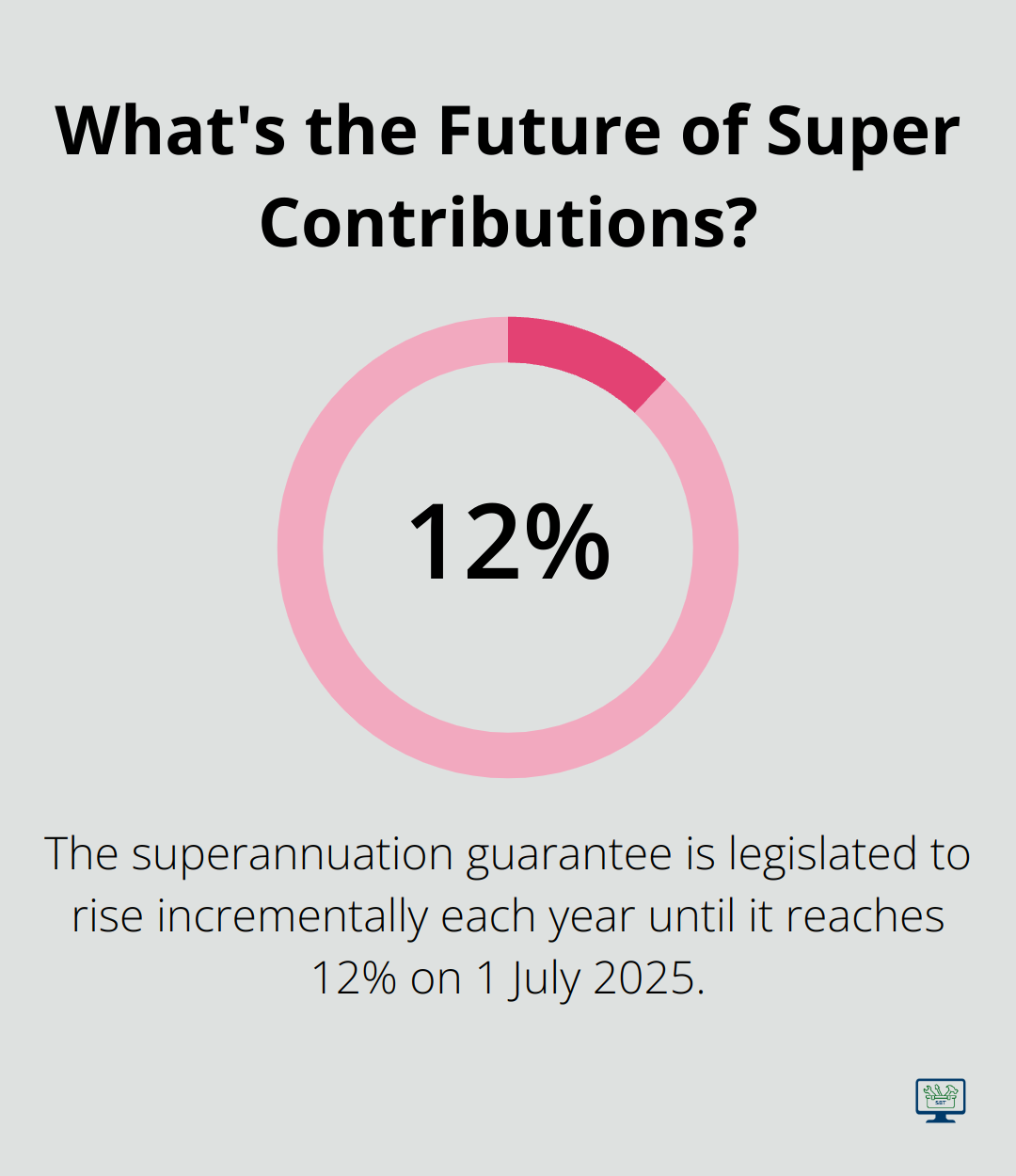
The superannuation guarantee (SG) requires employers to contribute to their employees’ retirement savings. The SG has been legislated to rise incrementally each year until it reaches 12% on 1 July 2025.
Key points for small business owners:
- You must pay super for employees who earn $450 or more per month (before tax).
- Super applies to overtime for some awards and agreements.
- Payments are due quarterly (strict penalties exist for late contributions).
To streamline your super obligations:
- Use accounting software that performs automatic super calculations.
- Set up a clearing house to distribute payments to multiple super funds.
- Consider offering salary sacrifice arrangements to employees (potential tax benefits).
Implementing Single Touch Payroll
Single Touch Payroll (STP) is now mandatory for all employers in Australia. STP Phase 2 will streamline reporting information about employees to government agencies. While it might seem challenging at first, STP can simplify your reporting processes.
Benefits of STP for small businesses:
- It reduces end-of-year reporting workload.
- It helps ensure compliance with tax and super obligations.
- It provides employees with real-time access to their payroll information.
To implement STP effectively:
- Choose STP-enabled payroll software (many providers offer affordable solutions for small businesses).
- Ensure your employee data is accurate and up-to-date.
- Establish a regular process for reviewing and submitting your STP reports.
Managing Payroll and Superannuation Efficiently
Efficient management of payroll and superannuation is essential for small business success. Consider these strategies:
- Use integrated payroll and accounting software (this can save time and reduce errors).
- Stay informed about changes in payroll tax and superannuation laws.
- Conduct regular audits of your payroll processes to ensure compliance.
Remember, while managing these obligations can be complex, the right tools and knowledge can make the process much smoother. SmallBizToolbox offers resources and guides to help you navigate these challenges effectively.
Final Thoughts
Small business taxes in Australia require diligence, knowledge, and strategic planning. Accurate record-keeping forms the foundation of effective tax management, ensuring compliance and helping identify potential deductions. Timely lodgment of tax returns and other required documents prevents penalties and maintains good standing with the ATO.

The Australian tax landscape changes frequently, with updates to rates, thresholds, and reporting requirements. Regular consultations with a qualified tax professional provide valuable insights and help optimize tax strategies. Many accounting software solutions offer features designed to handle Australian tax requirements, from GST calculations to Single Touch Payroll reporting.
SmallBizToolbox (https://smallbiztoolbox.com.au) offers comprehensive guidance on managing small business taxes and other aspects of running a successful enterprise. Our platform provides a range of tools and resources to support Australian small business owners in their growth journey. From AI-powered content creation to SEO optimization and expert insights, SmallBizToolbox equips you with the necessary support to navigate the complexities of small business management, including taxation.
FAQ
Q: What types of taxes are small business owners typically required to pay?
A: Small business owners usually need to pay several types of taxes, including income tax, self-employment tax, employment taxes, sales tax, and potentially property tax. Income tax is based on the profit generated by the business, while self-employment tax covers Social Security and Medicare taxes. Employment taxes come into play if you have employees, as you’ll need to withhold income taxes and pay payroll taxes. If your business sells taxable goods or services, you may also be responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax. Additionally, owning property used for business purposes may result in property tax obligations.
Q: How do I calculate my income tax as a small business owner?
A: To calculate your income tax as a small business owner, you first need to determine your business’s taxable income. This involves subtracting your business expenses from your gross revenue. After calculating your taxable income, apply the appropriate federal tax rates based on your business structure. Sole proprietors typically report their income on Schedule C of their tax return, while corporations file separately. It might also be beneficial to consult a tax professional to ensure you’re applying the correct deductions and credits to minimize your tax liability.
Q: Are there any tax deductions available for small business owners?
A: Yes, small business owners can take advantage of various tax deductions to reduce their taxable income. Common deductions include operating expenses such as rent, utilities, and salaries, as well as costs related to advertising, travel, and professional services. Additionally, home office expenses can be claimed if you use part of your home exclusively for business. Equipment purchases and vehicle expenses may also qualify for deductions, depending on their usage in the business context. Keeping thorough records and receipts throughout the year can help maximize these deductions when filing your taxes.
How useful was this Resource?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this Resource!
Tell us how we can improve this Resource?














