An SSL certificate (Secure Sockets Layer) is what makes your website show up as https:// instead of http://.
SSL encrypts the data sent between your website and its visitors, protecting things like contact forms, logins, and payment information.
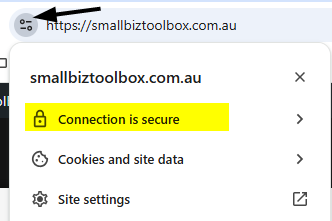
You can also click on the small Security icon to see more details of your website’s security status:
Today, SSL is essential for security, trust, and SEO.
Why SSL matters
- Security: Protects your site and your visitors from data theft.
- Trust: Visitors expect the padlock. Without it, many browsers show a “Not Secure” warning.
- SEO: Google confirmed HTTPS is a ranking signal. Sites without SSL may struggle to rank well.
- AI visibility: AI tools are more likely to trust and cite secure, HTTPS-based websites.
How to check your SSL
We’ll use a free tool:
👉 SSL Labs SSL Test
Step-by-step instructions
- Go to https://www.ssllabs.com/ssltest/analyze.html
- Enter your domain name in the Hostname box.
- Tick the box “Do not show the results on the boards” so your results aren’t made public.
- Click Submit.
- Wait for the scan to complete (it may take a few minutes).
- Review your results. You’ll be given a grade (A, B, C, etc.) along with details about your SSL configuration.
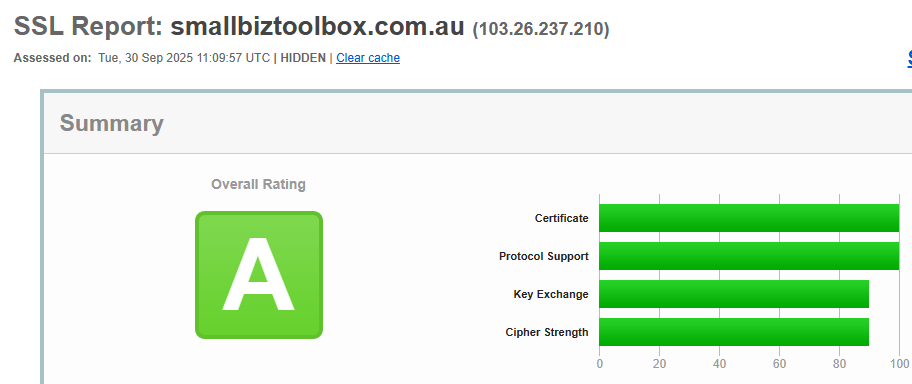
Apply this to your own website
- Record your SSL grade in your SEO Training Log.
- If your site is graded A: great! Your SSL is correctly configured.
- If your grade is lower, or if the tool says you don’t have SSL installed, speak with your web developer or hosting provider. Most reputable hosts now provide free SSL certificates (often via Let’s Encrypt).
You definitely want your SSL Certificate to be rated an “A”.
What it means if your SSL rating is not an “A”
When you run the SSL Labs test, the goal is to see your site graded A. This means your SSL certificate is installed correctly, is using up-to-date encryption, and your site is secure.
If your rating is lower than an A (for example B, C, or lower), here’s what it generally means:
- B Grade – Your site is reasonably secure, but there may be older protocols or weaker encryption methods still enabled. It’s not critical, but your developer or host should tighten the configuration.
- C Grade – There are significant issues. Your SSL might be using outdated ciphers, incomplete certificate chains, or older versions of TLS. Browsers may still connect, but security is weaker and this could undermine trust and SEO.
- D or lower – Your SSL setup has serious vulnerabilities or misconfigurations. Some browsers may even block access to your site with a warning. This urgently needs to be fixed by your developer or hosting provider.
- No grade / Fail – Your site does not have SSL at all. This means visitors will see “Not Secure” warnings, and search engines may penalise or avoid indexing your site.
What to do if your SSL grade is low
- Contact your hosting provider or web developer immediately. They can update your SSL certificate, disable outdated protocols, and reconfigure the server for stronger encryption.
- Ask about automatic renewals. Many SSL issues happen because certificates expire. Most hosts now offer auto-renewing SSL certificates (e.g. via Let’s Encrypt).
- Re-run the test after the fix to confirm your grade improves.

Need Help?
Go to our forum on this topic where other members or Ashley will help you.
Lesson outcomes
- Test whether your website is secured by SSL
- Understand why SSL matters for SEO, security, and trust
- Record your SSL status in your SEO Training Log
